Several textile composite solutions have been made with layers of 3D warp interlock fabric using para-aramid yarns or aromatic polyester yarns combined with three different types of architecture.
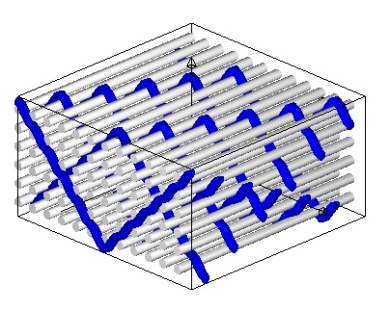
The first 3D warp interlock fabric architecture is:
3D warp interlock O – L 1-2-13 Binding {Plain weave}{1 13 – 2 14 – 3 15 – 4 16 – 5 17 – 6 18 – 7 19 – 8 20 – 9 21 – 10 22 – 11 23 – 12 24 – # – #} – Surface {Plain weave}{25 – # – # – # – # – # – # – # – # – # – # – # – 26 – #}
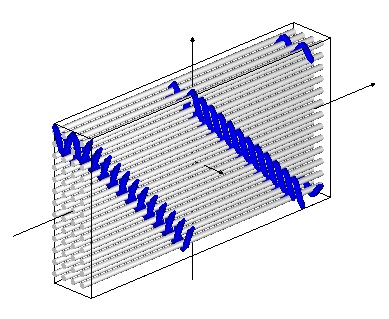
The second 3D warp interlock fabric architecture is:
3D warp interlock O – T 1-11-11 Binding {plain weave}{1 2 – #- #- #- #- #- #- #- #- #- #- #} – Stuffer {# – 3 – 4 -5 – 6 –7 – 8 – 9 – 10 – 11 – 12 – #}
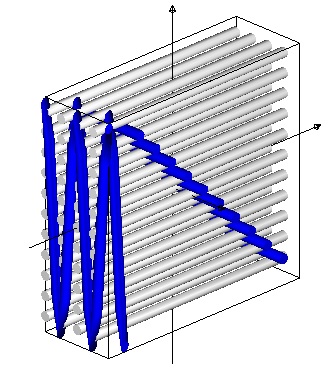
The third 3D warp interlock fabric architecture is:
3D warp interlock A – T 11-6-6 Binding {Pattern Twill 6 weft effect left shift (Pattern = {1 up 11 down – 6 down 1 up 5 down})}{1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 – # – # – # – # – # – #}
Protective solutions to FSP impacts (20 mm – 54 g) have been successful up to 630 m/s for architecture with orthogonal and layer-to-layer binding warp yarns.
composites à renforts Interlocks tissés. Application au blindage de véhicules. Thèse de doctorat. Valenciennes, France: Université de Valenciennes; 07/12/2011.
Boussu F, Veyet F, Lefebvre M. Recent advances in textilecomposite for impact protection. World Journal of Engineering. 2010; 7(1): p. 53-66.
Boussu F, Veyet F, Lefebvre M. Recent Advances in TextileComposite for Impact Protection. In NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Textile Composites; May 18-21, 2009; Kiev, Ukraine. p. 5 -6.
NATO Standardization Agency (NSA). STANAG 4569 Land (Edition1) – Niveaux de protection à assurer aux occupants des véhicules logistiques et des véhicules blindés légers. Norme. Brussels, Belgium:; 24/05/2004. Report No.: NSA/0533-LAND/4569.
Lefebvre M, Boussu F, Coutellier D. Study of impact behaviour ofthree warp interlock structures. Comparison with existing protections. In LWAG Light-Weight Armour for Defence & Security; March 2011; Haifa, Israël.
Lefebvre M, Boussu F, Coutellier D. Influence of warp interlockparameters on the ballistic behaviour of a structure. In 10th International Conference on Textile Composites; October 26–28, 2010; Lille, France. p. 322-328.
Lefebvre M, Provost B, Boussu F. Behaviour of warp interlockstructures under and IEDs attack, application to orthogonal and through the thickness warp interlocks. In NATO Advanced Study Institute “Defence Related Intelligent Textiles and Clothing for Ballistic and NBC (Nuclear, Biological, Chemical) Protection”; Tuesday 6th April to Friday 16th April 2010; Split, Croatia.
Lefebvre M, Boussu F, Coutellier D. Influence des paramètres detissage sur des structures interlock soumises à l’impact balistique. In JNC 17, Journées Nationales Composites; 15 au 17 Juin 2011; Poitiers, France.
Lefebvre M, Boussu F, Coutellier D, Vallee D. Influence of thegeometrical structures and resin rate inside composites structures on the ballistic behaviour under high velocity impact. In Mechanics of Nano, Micro and Macro Composite Structures; 18-20 June 2012; Politecnico di Torino, Italy.
Lefebvre M, Boussu F, Coutellier D, Vallee D. Influence of thevacuum resin process, on the ballistic behaviour of lightweight armouring solutions combining aluminium plates and warp interlock fabrics impacted with a Fragment Fragment Simulating Projectile. EPJ Web of Conferences. 2012; 26.
Phone: (+33) 320256476
Mobile: (+33) 626883959
E-mail : (click to reveal e-mail)